Create a random circular path
04 Dec 2018 • 0 Comments
- Introduction
- Obtaining a random circular area
- Clean the edges of the area with Cellular Automata, leaving only the outline
- Select the start and end points and find the path using DFS
Introduction
Two weeks ago, I had to find a non-overlapping circular path in a square grid. The requirements were as follows:
- circulation path (first == end)
- a clean 1 pixel line that does not overlap
- some randomness
Depending on the problem definition, we can also use the search algorithm like A*, but in this case I wanted to solve it in a simple and procedural way. Here’s how I made it.
- Obtaining a random circular area
- Clean the edges of the area with Cellular Automata, leaving only the outline
- Select the start and end points and find the path using DFS
The completed path is as follows. (Blue = start point)
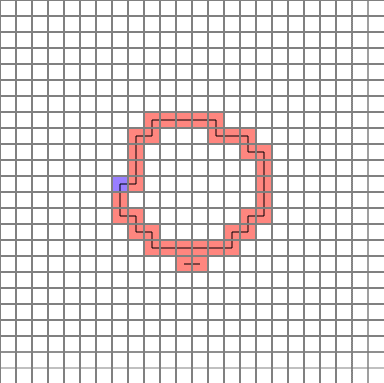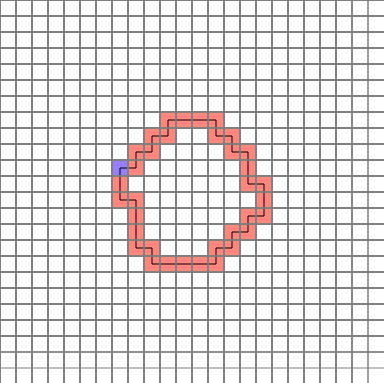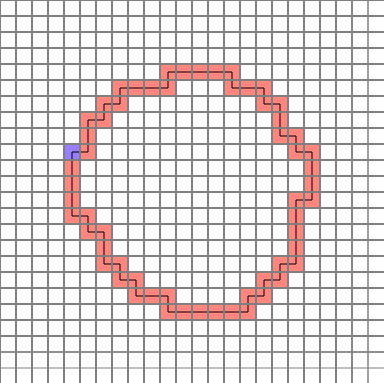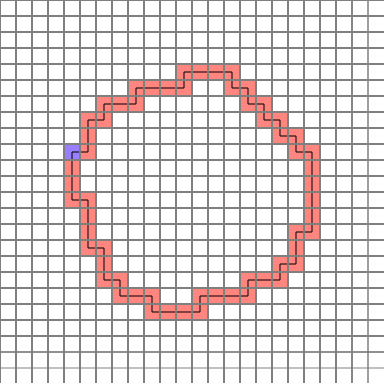
Let’s analyze them one by one.
Obtaining a random circular area
As you can see from the above gif file, the path is almost circular but it is not a perfect circle. I was wondering how to express a slightly deformed circle, but I remember a flash file that I saw very long ago (about 10 years ago).To find the value of the circle (\(\pi\)), use the Monte Carlo method to take a random point on the quarter circle. At this time, if the radius of the circle is r, you can get the value of \(\pi\) as follows.
\[\frac{Number\phantom{0}of\phantom{0}points\phantom{0}in\phantom{0}quarter\phantom{0}circle}{Total\phantom{0}number\phantom{0}of\phantom{0}points} \simeq \frac{\frac{\pi r^2}{4}}{r^2} = \frac{\pi}{4}\]I could not find the original. So, I added link to youtube video to find the circle area in a similar way.
So, like this idea, when you want to find a circle area, you can take a certain number of points in each cell that overlaps the circle area, and assign a probability value to the number of points belonging to the circle so that you can finally judge whether the cell belongs to the area Would not it be? I thought. Cells in the original circle will belong to the region with a 100% probability, but the cell at the edge will have different results every time it is executed.
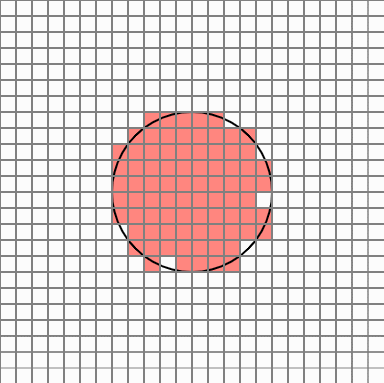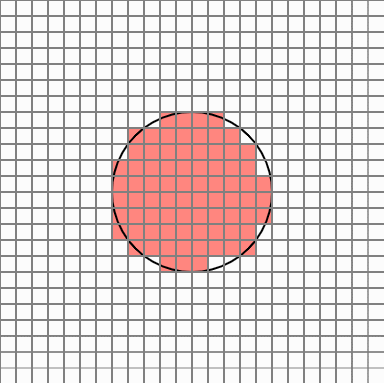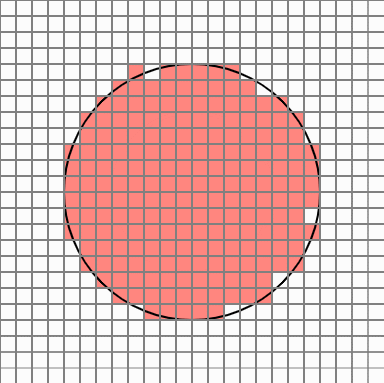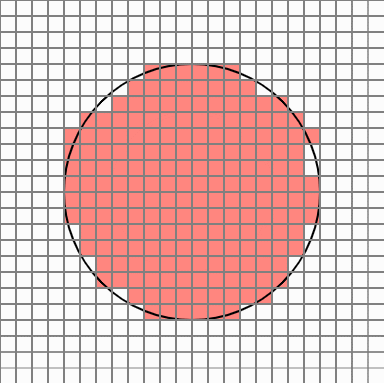
But in this case, there are too many cells popping out. Cellular Automata is a simple yet powerful PCG technique that allows smooth transition of these protruding edges.
Clean the edges of the area with Cellular Automata, leaving only the outline
Cellular Automata is an algorithm that changes its state according to a certain rule when each cell has a certain state in a cell grid.
In this case, once the number of neighbors is examined for eight directions of each cell, if there are three or less neighbors, the cell is eliminated. Repeat this process five times. Normally, the process is completed by repeating about two times.
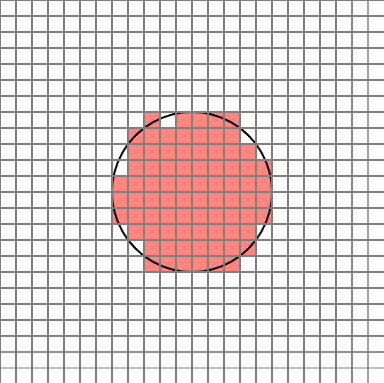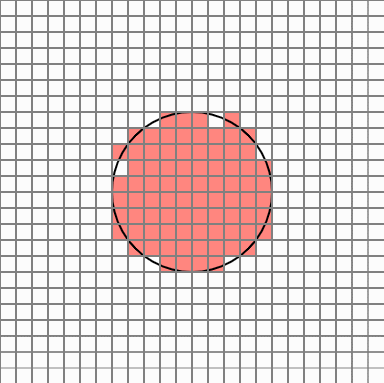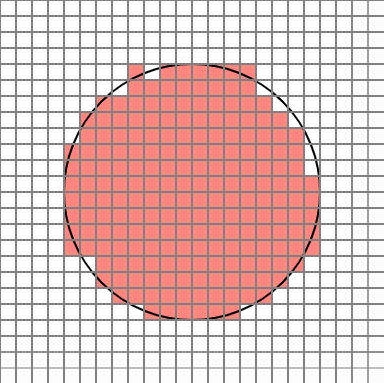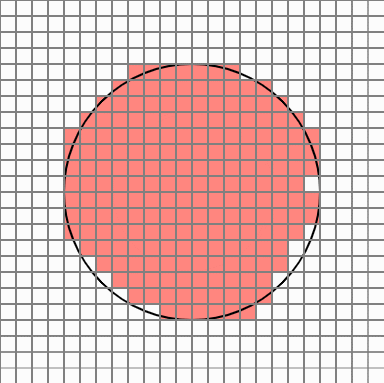
To leave the next outline, delete the cell with 8 neighbors in the 8 directions of each cell. This way you can eliminate the cell inside the circle.
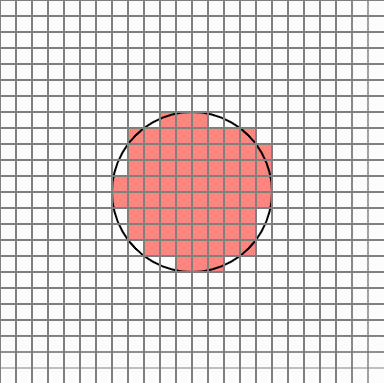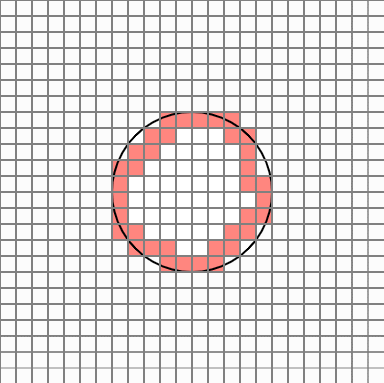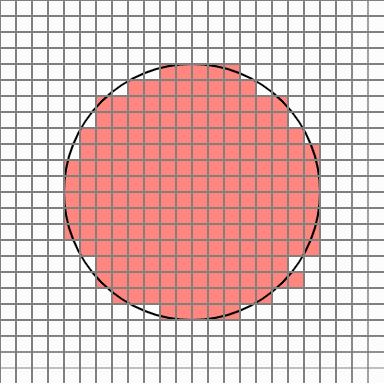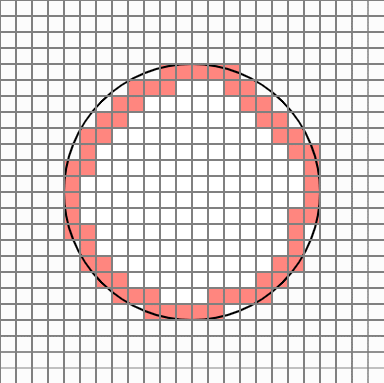
Now it seems to be plausible.
Select the start and end points and find the path using DFS
But the problem remains. In order to find the circular path of the circle, you have to select the starting point well. The starting point is preferably a cell with 3 or fewer neighbors, which reduces the chance of duplicate routes being formed. For the convenience of the algorithm, we set the end point to be the neighboring cell in the top, bottom, left, and right of the starting point.
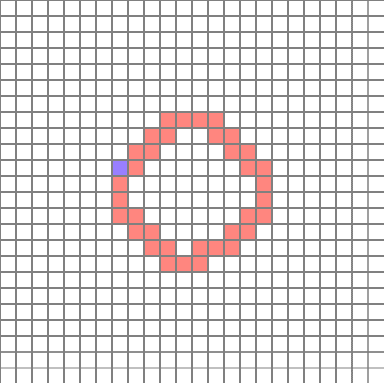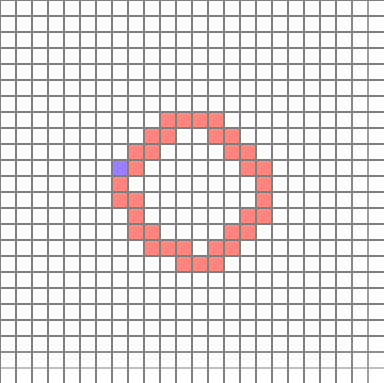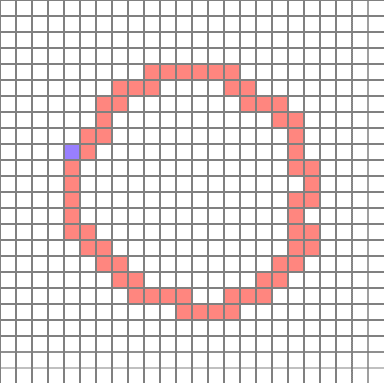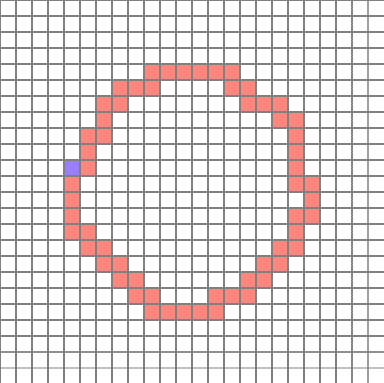 (The position is relatively constant because the cell is inspected sequentially, rather than at a random location, when determining the starting point. It is not a big deal because it will create a circular path anyway)
(The position is relatively constant because the cell is inspected sequentially, rather than at a random location, when determining the starting point. It is not a big deal because it will create a circular path anyway)
Now you can find the path with DFS. It inspects whether it is an endpoint by inserting and dropping cells one by one into the stack array. If it is not the end point, find the neighbor and put it on the stack if you have not visited the neighbor.
It is finished now. The picture file is the same as the one shown above.

I’ve never used markdown to write a blog, but it’s more fun than I expected. I have opened my blog so I have to work hard and study hard.